Lesson 1: The System Unit
“ We are using computer everyday without know what inside it and how it works.. ”
02 Apr 2016
By “ Syahmi Fauzi ”

What is System Unit?
- Also known as a computer chasis (system chasis), computer case or computer tower
- A container that houses electronic components to make up a computer
- To protect the sensitive electronic parts from the outside elements

Four most common types of personal computers:
Desktops
- Desktop system units located in separate case, called tower unit (or tower computer)
- Has vertical system unit
Laptops
- Laptop (notebook) system units are portable and much more smaller than desktops
- Ultrabooks (ultra-portables or mini notebooks) are lighter, thinner and have longer battery life than other laptops
Tablets
- Tablet system units (tablets computers) are located behind the monitor
- Smaller, lighter and generally less powerful than laptops
- Use a virtual keyboards
Mobile Devices
- Mobile devices (handheld computers) smallest and fit comfortably in one hand
- The most popular type of personal computer
- System units located behind the display screen (monitor)
Components
Similar basic components in all types of personal computer mention above are:
- System Board
- Microprocessor
- Memory
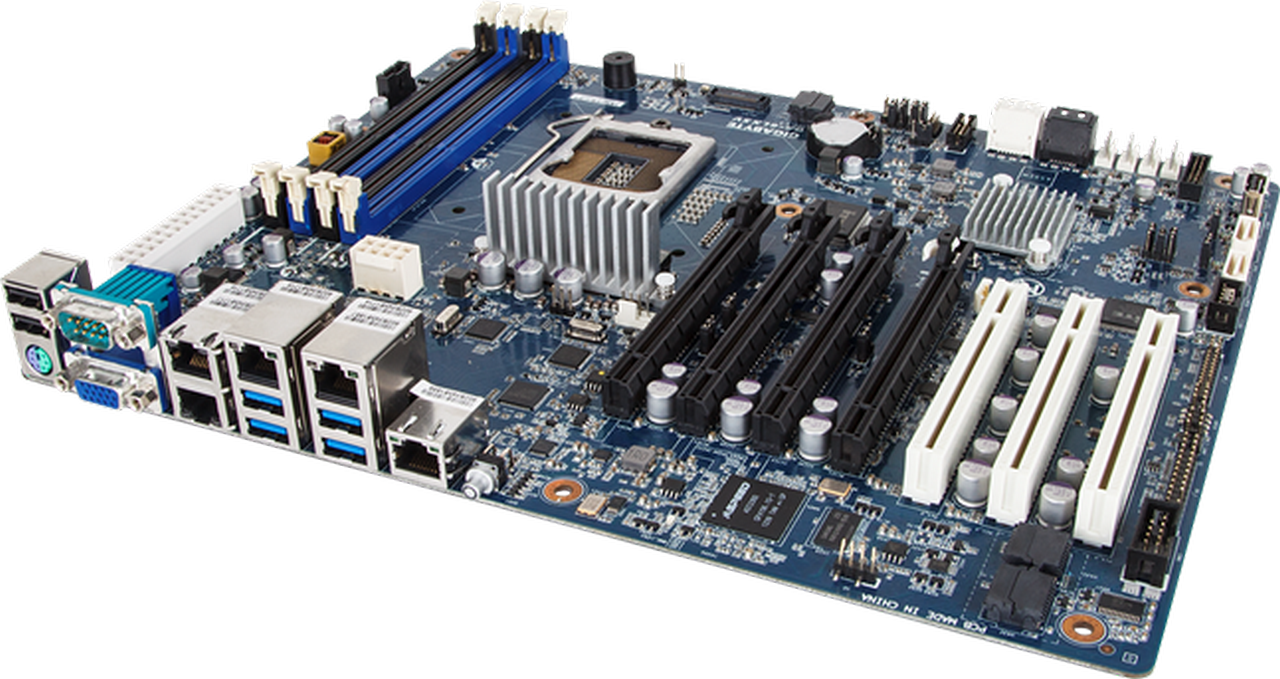
System Board
- Other names - mainboard or motherboard.
- Controls all communication for the computer system.
- Connect with all external and internal devices and components
- Sockets - provide connection points for chips (silicon chips, semiconductors, integrated circuit).
- Slots - provide connection points for specialized card or circuit board.
- Bus lines - provide pathways to support communication.
Microprocessor

In most personal computers, the Central Processing Unit (CPU) or processor is contained on a single chip called the microprocessor. It has two basic components:
- Control Unit (CU)
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Memory
Holds data, instructions and informations
Three type of memory chips:
- 1) Random Access Memory (RAM)
-
Volatile or temporary memory (storage) because their contents are lost if power is disrupted.
- Cache memory is a high-speed holding area for frequenly used data and information.
- DIMM is used to expand memory.
- Virtual memory devides large programs into parts that are read into RAM as needed.
- 2) Read-Only Memory (ROM)
- Non-volatile memory and control essential system operations.
- Information stored by manufacturer
- 3) Flash Memory
- Combination of both RAM and ROM
- Does not lose its contents when power is removed

Expansion Slots & Cards
Most computers allow users to expland their systems by providing expansion slots on their system boards to accept expansion cards.
Examples of expansion cards:
- Graphics Cards
- Sound Cards
- Network Adapter Cards/Network Interface Cards (NIC)
- Wireless Network Cards
Bus Lines
- Also knows as buses
- Provide data pathways that connect various system components
- Bus width - the number of bits that can travel simultaneously
- System buses - connect CPU and memory
- Expansion buses - connect CPU and slots
Expansion Buses
Three types of principal expansion buses:
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) can connect from one USB device to another)
- Firewire bus is similar to USB bus but more specialized.
- PCI Express (PCIe) bus provides a single dedicated path for each connected device.
Ports
- Connecting sockets on the outside of the system unit
Four standard ports are:
- Video Graphics Adapter (VGA) and Digital Video Interface (DVI) - provide connections to system unit
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) - to connect keyboards, mice, printers and storage devices
- Firewire - provides high-speed connections to Firewire devices between devices and perconal computer such as camcorders and storage devices
- Ethernet - high-speed networking port for Local Area Network (LAN) that has become a standard for many of today's computers
Five speciality ports are:
- External Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (eSATA) - for high-speed connection to large secondary storage devices.
- High Definition Multimedia Interfave (HDMI) - for high-definition digital audio and video.
- Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) - for digital music.
- Mini DisplayPort (MiniDP. mDP) - for large monitors.
- Thunderbolt - for high-speed connections to up to seven separate devices connected one to another.
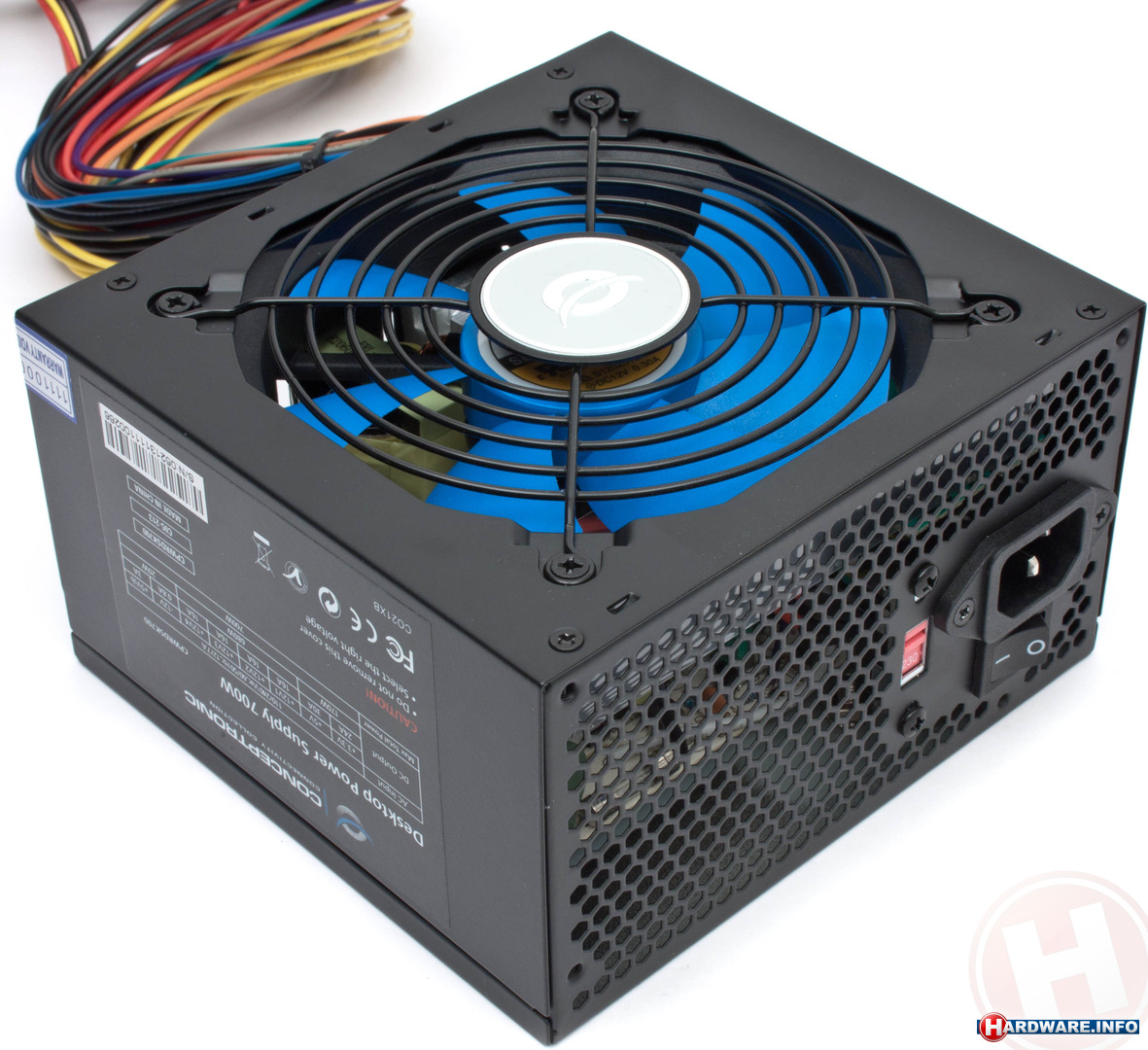
Power Supply
- Convert Alternating Current (AC) to Direct Current (DC)
- Supply electrical energy to our personal computer

Source:
Computing Essentials 2015
By:(Timothy J./Linda l./Daniel A.)O'Leary